If your cat is breathing fast, it can cause immediate panic. The normal respiratory rate for a healthy cat is between 20 to 30 breaths per minute. Use a stopwatch or Smartphone to count the breaths. If your cat’s breathing exceeds this, it could be a sign of a serious condition.
Rapid breathing can indicate your cat isn’t getting enough oxygen. If they’re lethargic or breathing rapidly while at rest, it’s important to call the vet. Staying vigilant for other symptoms is crucial to avoid a potential emergency.
Why is My Cat Breathing Fast? (Short Answer!)
Types of Heavy Breathing in Cats
Types of Heavy Breathing in Cats cover various breathing issues that could indicate serious health problems, requiring careful observation.
Cat Panting
Panting is not normal for cats like it is for dogs. If your cat is panting after playing, it could be a sign they are overheated or extremely stressed. While it may not seem dangerous, it’s important to figure out the situation and improve it.
Wheezing and High-Pitched Sounds
Wheezing is a sign of partial airway blockage, often linked to feline asthma. Cats with wheezing usually make high-pitched sounds when they exhale. This could mean their airways are narrowing, which requires attention.
Rapid Breathing
If your cat is breathing fast, it might not be getting enough oxygen or releasing enough carbon dioxide. Exercise, lung disease, or heart disease can cause rapid breathing. A healthy cat should return to normal with rest.
Signs to watch for:
-
- Tachypnea (rapid breathing)
- Difficulty breathing or abnormal chest movements
Labored Breathing
When a cat has labored breathing, it may be using its abdomen more to breathe. This indicates they are struggling, and you may notice them taking deeper breaths or open-mouth breathing. If this happens, it’s time to see a vet.
Noisy or Raspy Breathing
Noisy breathing can occur if air passes through a narrow airway. Problems with the nasal passages, pharynx, or trachea might cause this. If your cat’s breathing sounds raspy or noisy, check for underlying issues like respiratory tract problems.
Heavy Breathing While Resting
Heavy breathing in cats should only happen after strenuous exercise. If your cat is breathing heavily while resting, aside from a deep sigh, it could be due to heart failure or severe lung disease. Always monitor their behavior closely.
Shallow Breathing
Cats can have shallow breathing, but if combined with other symptoms like rapid breathing or open-mouth breathing, it becomes a concern. Keep an eye out for any signs of difficulty or labored breathing.
Signs of Heavy Breathing in Cats
When your cat is gagging or breathing fast, it can signal an illness. You might notice the sides, chest, and stomach moving rapidly. Other signs include open mouth breathing or panting, along with a lowered head and extended neck.
Noisy Breathing
If your cat shows noisy breathing, you might hear whistling, wheezing, or groans. This can happen along with coughing and gagging. Such sounds are serious and can indicate breathing difficulties.
Lethargy and Blue Gums
Watch for signs like lack of energy or lethargy. If your cat has blue gums, it may be struggling to get enough oxygen. These are serious health concerns and should prompt a visit to the vet.
Reluctance to Move
If your cat seems to have a reluctance to move, jump, or play, it could be due to breathing difficulties. Extended periods of sleep and loss of appetite can also indicate that something is wrong.
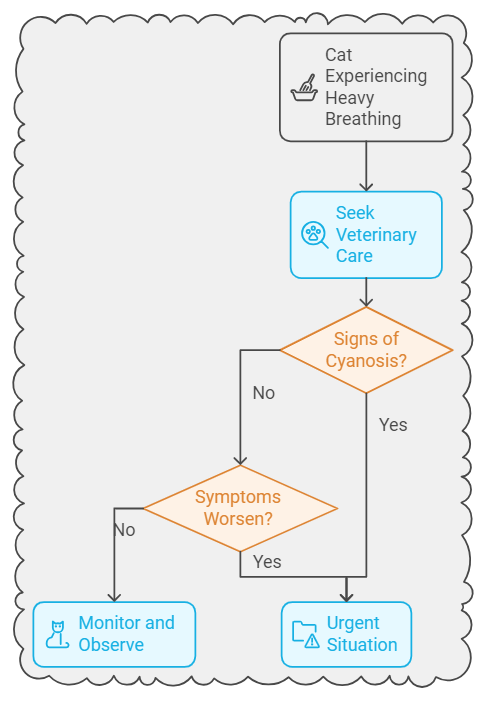
Medical Emergency
Difficulty breathing is a medical emergency. If your cat’s breathing rate is higher than 30 breaths per minute, it could be a sign of heart failure or other serious issues. It’s vital to seek veterinary care for your kitty.
Rapid Breathing
You may notice the rapid rising and falling of the stomach and chest. If your cat is panting with an open mouth, it may feel anxious or panicky. Observing these symptoms can help you catch problems early.
Underlying Health Problems
Fast breathing is often a sign of an underlying health problem. Watch for any abnormal respiratory sounds like wheezing or coughing. If these symptoms persist, don’t hesitate to consult your vet.
Causes of Heavy Breathing in Cats
Your cat may breathe fast due to asthma, causing airway inflammation, or heartworms, which block the lungs. Other causes include bacterial infections, trauma, or chest injuries that lead to fluid buildup. Stress or anxiety can also trigger rapid breathing. If your cat is scared or shows additional symptoms, consult a Vet for guidance.
Asthma and Allergies
Asthma can make a cat’s breathing quick and labored. This happens due to inflammation in the airways, causing wheezing or coughing. If your cat is not eating or seems uncomfortable, it’s essential to talk to a Vet about possible corticosteroids or bronchodilators.
Heartworms and Infections
A bite from a mosquito can introduce heartworms into your cat’s respiratory system, leading to labored breathing. These parasites can cause fluid buildup in the lungs, making it harder for your cat to breathe. Bacterial infections, like pneumonia, can also lead to panting and a higher respiratory rate.
Trauma or Injuries
Trauma to the chest can cause serious problems like fluid accumulation in the chest cavity, leading to fast breathing. Injuries can affect the lungs or even lead to bleeding and pain, making breathing difficult for your pet. Always consult a Vet if your cat is scared or appears to have trouble breathing after an accident.
Stress and Anxiety
Sometimes, stress or anxiety, much like abortion in cats, can cause rapid breathing. A scared cat may show signs of rapid breathing, much like we experience when anxious. It’s important to check for other symptoms like cat diarrhea or the need to check cat’s temperature to rule out deeper issues.
What to Do If Your Cat is Breathing Fast?
If your cat is breathing fast, a veterinarian will likely begin by stabilizing them using oxygen therapy. The vet may run diagnostic tests like a blood chemistry panel, urinalysis, and chest X-rays to pinpoint the underlying problem. During the physical exam, your cat’s lifestyle, health, and symptoms will also be assessed.
Treatments depend on the diagnosis. For asthma or chronic bronchitis, vets may prescribe medications to reduce inflammation and dilate airways. Be sure to remove secondhand smoke, dusty cat litter, and strong scents from your home, as these worsen respiratory issues.
In cases involving heartworms, prevention is key because heartworm disease can be tough to treat. For infections, vets may prescribe antibiotics, whether it’s a bacterial, fungal, or viral infection. Cancer treatments may involve surgery, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy to improve your cat’s well-being.
- If your cat has fluid buildup from heart disease, a chest tap or chest tube might be needed to improve breathing.
- For trauma-related issues, your cat may require cage rest, pain relief, and even surgery to recover.
In a medical emergency with consistently fast breathing, contact your vet or go to an animal hospital immediately. The vet will evaluate your cat’s condition, checking for heart murmurs, fluid in the lungs, and other critical signs.
If your cat’s rapid breathing subsides, keep a journal of symptoms, noting triggers and duration to share with your vet. This helps narrow down the cause and guide future treatment plans.
Bottom Line
When your cat’s breathing becomes rapid or heavy, it’s essential to act quickly and seek veterinary care. Getting treatment at a veterinary hospital can help if the issue is diagnosed early. This often involves nursing care, oxygen therapy, or fluid therapy. The sooner the cause is found and treated, the better the chances of a speedy recovery.
- Keep your cat monitored at home and ensure they stay indoors.
- Ask your veterinarian if you have any concerns about symptoms.
- Balanced, healthy diets and regular veterinary checkups can help prevent future health issues.
Watching out for signs and acting with caution can protect your cat’s health and help avoid severe conditions in the long run.
FAQs
Why does my cat breathe fast while resting?
Your cat may breathe fast due to lung disease, heart disease, or upper respiratory tract issues. Metabolic conditions, like uncontrolled diabetes, high body temperature, pain, stress, or blood disorders can also be causes.
How can I treat my cats’ rapid breathing at home?
If your cat has heavy breathing from a viral or bacterial infection, using steam or humidifiers can help. These can loosen mucus and ease nasal breathing as your cat recovers. If the infection gets worse, it may need to be treated with antibiotics.
Should I be worried if my cat is breathing hard?
Cats may pant or show heavy breathing as an indication of a serious health concern that requires prompt veterinary care, especially if it’s sudden or unusual.
Why is my cat’s stomach moving like a heartbeat?
A forceful blow or injury can cause a diaphragmatic hernia, leading to labored breathing, rapidly moving abdomen, and irregular heartbeat as signs of shock, while other symptoms like vomiting, diarrhea, or an empty feeling may occur due to damage to the bowel or stomach.